Reading Time: 8 minutes 🍃
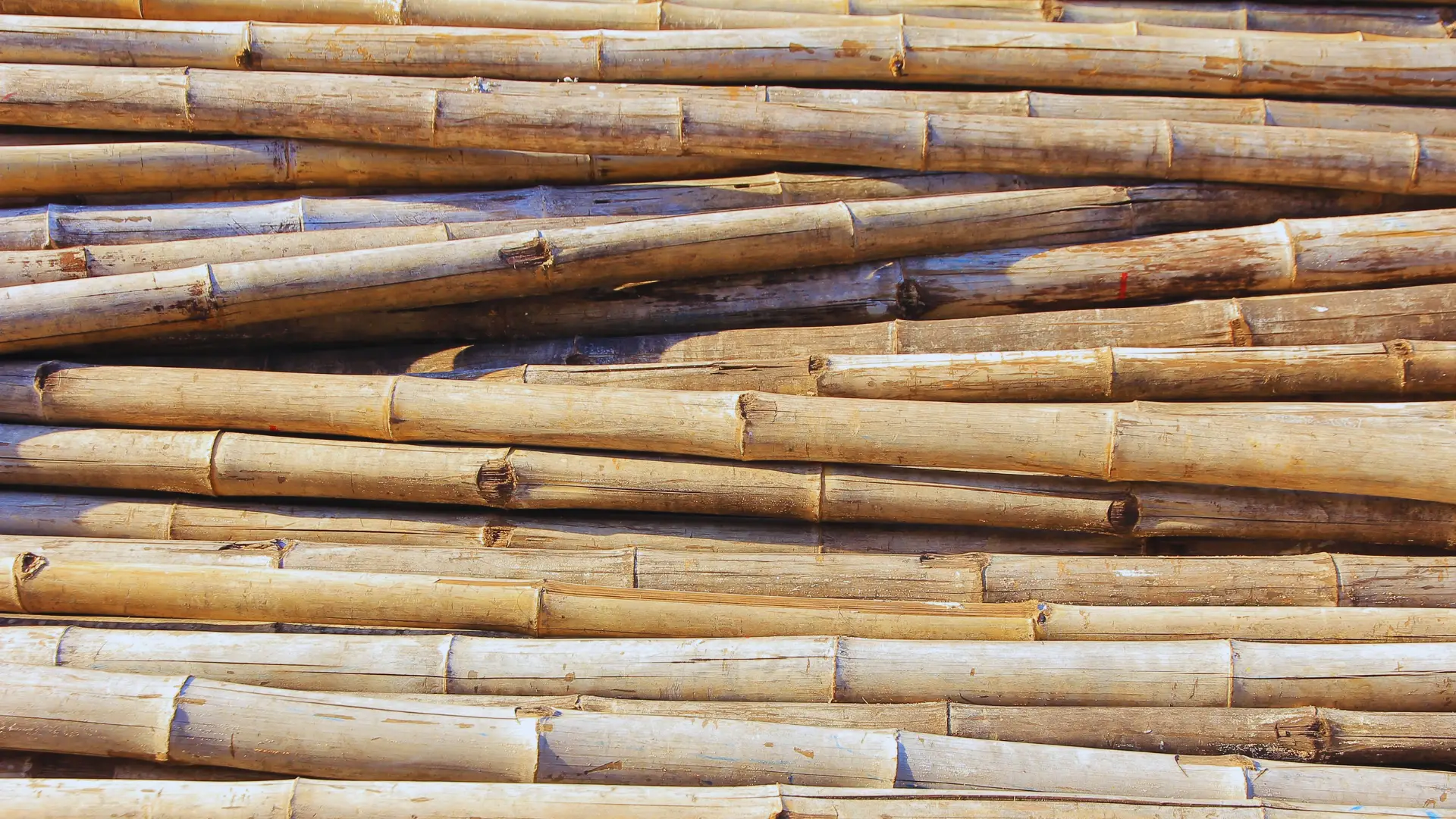
Bamboo is a versatile plant with remarkable properties. People and livestock eat shoots and seeds, and wild animals forage on bamboo, eating the leaves and tender shoots. Bamboo is used to construct houses, build boats, make paper, cutting boards, and even cups.
It is used in traditional Chinese medicine. The question that must be answered is what can be done with bamboo products once they are broken or used up. Can you compost bamboo, and will it break down sufficiently?
Bamboo can be composted. The leaves and living plants make up the green waste which will decompose quickly. Old or dried plants and bamboo products are composted as brown material, which takes longer to compost. Bamboo helps add silica, leading to improved plant and soil health.
Bamboo is well-known for its strength and flexibility, making it suitable for manufacturing various items, including scaffolds and buildings. Many people think that this feature of bamboo makes it ineligible for composting.
Can You Put Bamboo In The Compost?
Bamboo can be composted as it is a plant and, therefore, organic material capable of decomposing and forming compost.
Bamboo is a perennial plant from the family Poaceae, which comprises tall grass-like trees. It is native to Asia but is grown in many countries throughout the world.
Bamboo is popular with gardeners as it makes a good screening and ornamental plant. Many species of bamboo can become invasive and require trimming and pruning to keep them from taking over the garden. Leaves and new shoots may need to be removed.
The cuttings from bamboo must be disposed of somehow, and the obvious solution for many gardeners is to compost this garden waste.
Bamboo paper and paper towels are produced as they are an eco-friendly alternative to many paper products. Bamboo containers are replacing polystyrene in many fast-food restaurants. All of these bamboo products must be disposed of, and they can be usefully added to compost.
Bamboo Provides Two Types Of Compost Material
Compost materials are divided into two categories. Brown waste material is dry organic material. In the case of bamboo, it includes bamboo paper products, bamboo utensils, and any items made from bamboo. All dry bamboo is classified as brown waste.
Brown material is important for composting as it provides carbon for decomposition. Carbon provides energy for the chemical activity required to break down plant materials in the compost.
Green wet bamboo cuttings or plants removed from the garden make up green waste for composting bins and heaps. Green material provides critical nitrogen, which oxidizes the carbon as part of the composting process. Green material is always bamboo which has recently been alive.
How To Compost Green Bamboo?
Green cuttings of bamboo should be shredded to increase the rate of decomposition. Leaving the cuttings in large pieces will take longer to compost. This could result in odors and take up more of the gardener’s time managing the compost heap.
Green waste material must be layered with brown waste. It should be kept moist and turned regularly. Green bamboo waste can take two to six months to decompose, depending on the thickness of the waste.
Here is a video that shows you some quick tips for managing bamboo leaves and cuttings for composting.
How To Compost Brown Bamboo Waste?
Bamboo is used to construct a wide range of objects, from chopping boards to buildings. Bamboo is strong because it contains a lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose matrix. This makes it extremely resilient while not being overly rigid. The chemical bonds allow bamboo to have some degree of flexibility.
Bamboo grows in long hollow stems known as culms. The hollow interior makes bamboo very light, an advantageous feature of using it as a construction material.
Bamboo culms can become very thick, and some people might worry about composting such a large piece of plant material. Brown waste bamboo takes much longer to decompose than green bamboo waste. Brown bamboo material takes about six months but may take as long as three years if the material is thick.
Brown bamboo waste should be shredded to increase the surface area for the composting process. The lignin in bamboo does not decompose by the action of the composting bacteria.
Lignin must first be exposed to fungi that dissolve the lignin bonds and soften the matrix. Only once this has occurred can the composting bacteria begin work on the brown bamboo waste.
Brown bamboo waste must be layered with green material to allow for sufficient energy and elements for composting.
Can You Compost Bamboo Toothbrushes?
Bamboo toothbrushes have become popular with people concerned about protecting the environment. Toothbrushes made with plastic are non-biodegradable, and when discarded in landfills, they cause pollution and unnecessary inorganic waste.
Bamboo toothbrushes usually have nylon bristles. Nylon is a synthetic material that does not compost. The bristles must first be removed to add bamboo toothbrushes to the compost. The rest of the toothbrush can be cut into smaller pieces using gardening shears and added to the compost.
Some bamboo toothbrushes have boar hair bristles, but these are rare. These toothbrushes do not need to have the bristles removed as they are made from organic material that will compost. The entire toothbrush can be cut smaller and added to the compost.
Can You Compost Bamboo Clothing?
Bamboo fabric has become a popular choice for eco-friendly clothing. It is odor-proof, as bamboo has antiseptic properties. It is also a breathable fabric that helps the wearer stay cool. Surprisingly bamboo fabric is soft and comfortable to wear.
Bamboo is a renewable source for clothing manufacture, and the clothes can be composted once worn out. Unfortunately, zippers, clasps, and other fasteners may be attached to bamboo clothes that cannot be composted.
It is necessary to remove all non-compostable fittings before adding the clothing to the compost heap. Shoes made from bamboo canvas must be investigated to determine the composition of the sole. The whole shoe can be composted if the shoe sole is made from an organic substance such as cork.
If the sole is made from rubber or plastic, the sole should be removed from the shoe uppers. The fabric part of the shoe can be composted, but the sole must be recycled in a rubber or plastic recycling plant.
The discarded bamboo shoes should be cut into small segments for composting to hasten the process.
Can You Compost Bamboo Toothpicks And Skewers?
Bamboo toothpicks and skewers are ideal brown waste materials for composting. They are thin and only need to be broken into smaller pieces to speed up the process. Chopsticks are commonly made from bamboo and can also be composted.
Can You Compost Bamboo Cotton Buds?
Bamboo cotton buds are made from two organic materials; bamboo and cotton. As a result, bamboo cotton buds are fully recyclable and can be cut up and added to the compost.
Can You Compost Bamboo Cups And Plates?
Bamboo cups and plates may be compostable, but much depends on how the utensils are manufactured. Some bamboo cups and plates have adhesives or water-resistant finishes, which may make them unsuitable for composting.
Bamboo is sometimes combined with melamine in the manufacture of cups and plates. These bamboo products cannot be composted and must be disposed of alternately.
Bamboo cups and plates made with only eco-friendly products can be composted. It is essential to check the labels and manufacturing details when buying items. This will give you the necessary information to know if the utensils can be composted.
Can Bamboo Straws Be Composted?
Plastic straws have become a pollution nightmare. It is believed that more than eight million straws pollute beaches worldwide. This figure applies only to the beaches. It is much higher when considering pollution across the land.
Bamboo straws have become an alternative to the use of plastic straws. Bamboo straws are compostable if they are made entirely from bamboo.
Some bamboo straws have a polymer coating to make them more durable and waterproof. These bamboo straws cannot be composted as the polymer will not decompose.
Can You Use Bamboo In Vermicompost?
Bamboo, which does not have any adhesives or toxic substances, can be used in vermiculture to create vermicompost. Bamboo that has any substances that may be toxic to the worms should not be included in the worm bin, as they will harm and possibly kill the worms.
The bamboo should be shredded to make it more easily accessible to the worms used in the vermiculture. It is best to mix the shredded bamboo with cow manure and let it begin decomposing before adding it to the worm bins.
This makes the bamboo easier for the worms to break down and pass through their bodies to create vermicompost. Researchers found that worms fed bamboo grew faster and reproduced more quickly.
Can You Use Bamboo As A Mulch?
Mulches using organic materials can be seen as a slow process of composting while reducing the water loss from the soil around plants.
Bamboo is an organic material that is slow to decompose in normal circumstances. It can be used as a mulch around plants to prevent weed growth and moisture loss.
The bamboo should be cut into pieces or chipped but not shredded. The bigger pieces will take longer to decompose than shredded bamboo. It will act as a mulch around the plants while decomposing very gradually.
Bamboo is a fast grower, so using bamboo mulch is sustainable if you have bamboo in your garden that needs to be cut back regularly. You will have a steady supply of mulch to replace any bamboo mulch that decomposes.
Check out: Bamboo Leaves As Mulch
What Are The Pros Of Composting Bamboo?
Composting bamboo has numerous benefits.
- Composting bamboo garden waste removes the waste while providing compost for the garden.
- Compost containing bamboo provides a good source of free nutrients for plants. It is a cost-effective way of feeding garden plants and crops.
- Composting bamboo products reduces the strain on landfills.
- Composting bamboo is eco-friendly and reduces a person’s carbon footprint.
- Bamboo contains high levels of silica which are released into the compost.
Why Do Plants Need Silica In Compost?
Silica is a trace element necessary for plant health, making it a valuable addition to compost. The silica is converted to silicic acid by the microbes. When silica-rich compost is used on plants, they absorb silicic acid through their roots.
Silica allows plants to withstand droughts and frost better. It strengthens the plant cell walls, reducing water loss. The stronger cell walls make the plant more resilient to frost.
Researchers have shown that adding silica to crops increases the yield significantly. Silica also aids the plant by assisting it in the uptake of other mineral elements such as nitrogen, potassium, molybdenum, phosphorous, and zinc.
Silica enhances root growth, allowing new plants to become established more quickly. Root growth in older plants is better when there is access to silica, ensuring the plant stays healthy.
Silica improves the production of chlorophyll, improving the plant’s ability to photosynthesize to produce sugars and oxygen.
It can be seen from this evidence that using bamboo in compost is highly beneficial. The nutritional quality of the compost is increased, making it better for application to plants.
What Are The Cons Of Composting Bamboo?
- Bamboo is a material that takes longer than some others to compost. This is especially true if the bamboo is in larger pieces. Gardeners may wish for faster compost production and prefer to leave bamboo waste out of their compost.
- Shredding or cutting bamboo into small pieces can be time-consuming.
- Bamboo may sprout in the compost heap. To avoid this, all bamboo roots or rhizomes must be thoroughly shredded.
Conclusion
Bamboo can be composted as long as it does not contain toxic substances. It is a beneficial plant material to include in compost as it adds silica which is highly beneficial to plants. It is an excellent waste material to feed worms in vermiculture, producing vermicompost.
Sources
- https://www.britannica.com/plant/bamboo
- https://www.nature.com/articles/srep11116
- https://thescientificgardener.com/can-you-compost-bamboos-how
- https://agsolutions.com.au/2019/08/09/silica-overlooked-element/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337735989_Bamboo_Bambusa_polymorpha_Leaf_Litter_as_a_Vermiculture_Substrate_for_Earthworms_Pontoscolex_corethrurus_Muller_and_Drawida_assamensis_Stephenson
Recent Posts
Poinsettias tend to return to our collective memories around Christmas time. They’re a beautiful red and can be a bit difficult to take care of. Would it be possible to help poinsettias grow with...
There’s nothing more satisfying than a nice cool, juicy strawberry on a hot afternoon in June. Strawberries are a favorite fruit to many, so much so that people have taken it upon themselves to...

